How to Design and Deploy A Wireless Network
When designing and deploying a wireless network, there are several factors to consider. Most manufacturers of wireless access points and routers indicate a typical range that their equipment can provide. Depending on the type of antenna used and the physical location of the access point or router, the range may vary significantly. It is important to consider obstacles such as walls, ceilings, furniture, and electronic interference from machinery, power lines and even microwave ovens as these all play a role in wireless signal reception. In wireless transmissions, reflections (when wireless signals “bounce” off objects) and multipath (when wireless signals travel in multiple paths arriving at the receiver at different times) are as important as signal strength in determining the success of an installation. A signal will also exhibit peaks and nulls in its amplitude and alteration of its polarization (vertical or horizontal) when propagating through walls, ceilings and reflecting off metallic objects.
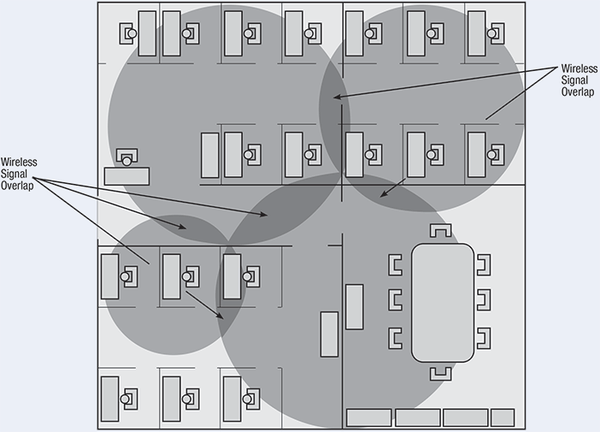
Wireless radios have special hardware and software to deal with multipath and signal level nulls, but if the antenna is in a poor location, the radio will not be able to communicate. When trying to get the best performance in a location with a lot of barriers or reflections, it is important to be able to move the antenna in all three axes in order to minimize the effects of multipath and optimize the signal strength. A good first step is to obtain a layout of the floor plan and then draw in access point locations. You will want to “overlap” the range of the access points so you have complete coverage.
Antenna Position: Directional
Yagi and parabolic grid antennas, typically used for point to point line of sight applications, must point directly at one another for maximum signal strength. Be sure to clear all obstructions that could distort or block the antenna beam.

Antenna Position: Omni-Directional
Omni-directional antennas should be mounted as far away as possible from all surfaces including walls, floors, ceilings etc. Additionally all Omni-directional antennas should be mounted at the same height for maximum performance and signal strength.

