Radio Frequency Explained
RF, radio frequency, is an electromagnetic wave between 1 MHz and 3 GHz used in wireless networks to transmit video, voice and data. They can also be used for AM radio broadcasting, navigational beacons and shortwave radio. Waves from 3 GHz to 30 GHz are microwave frequencies used for FM radio, aviation communications, radar and satellite links. Millimetre wave frequencies range from 30 GHz to 300 GHz and are used to transmit large amounts of data and simultaneous voice or video. RF waves can be transmitted through different media such as coaxial cable, a circuit board or through an antenna.
There are three main attributes to consider for RF waves: frequency, wavelength and Hertz. Frequency is the number of electromagnetic wave cycles that pass a specific point per unit of time. Wavelength is the distance after which the electromagnetic wave fields repeat themselves. Hertz is a measurement of the wave cycles per second.
1 Hertz (Hz) = 1 wave/ 1 second
1 Kilohertz (kHz) = 1 thousand waves/ 1 second
1 Megahertz (MHz) = 1 million waves/ 1 second
1 Gigahertz (GHz) = 1 billion waves/ 1 second
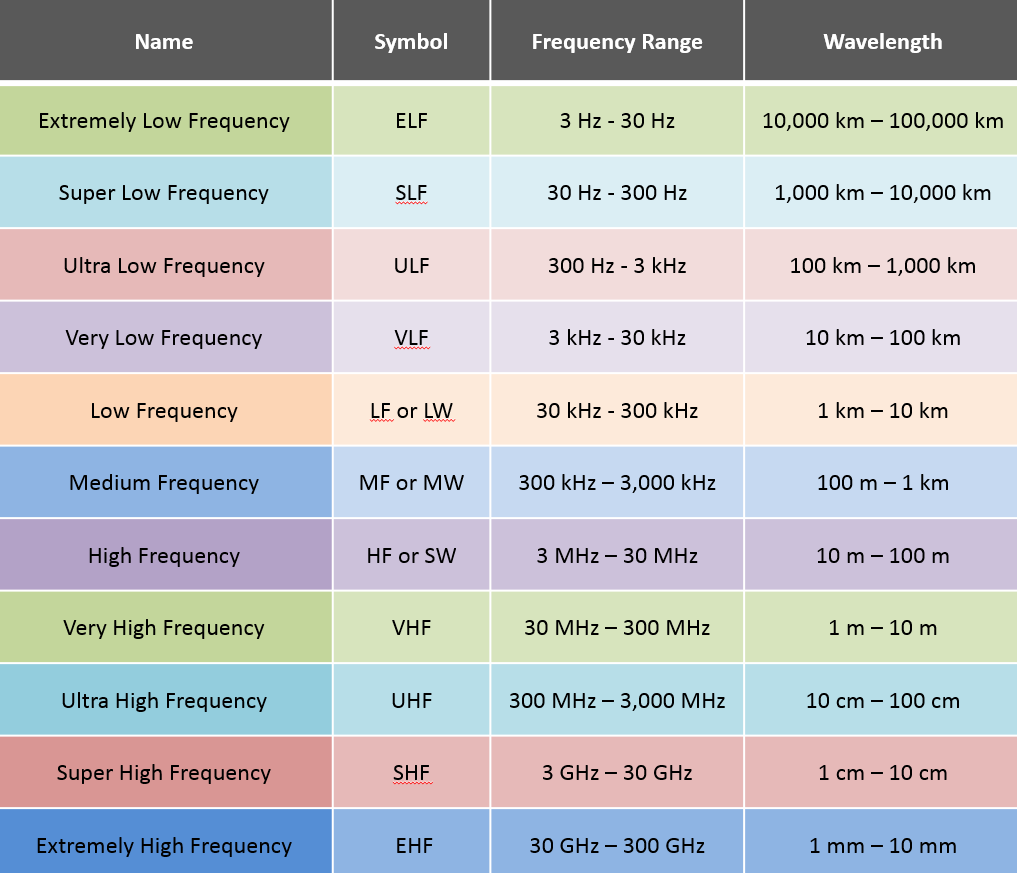
To get a better idea of this, and for a handy reference, here is a chart of RF frequencies: